この記事では以下の内容を学びます:
- – 会話内容をデータベースに永続化する本番環境対応AIエージェントの構築方法
- インテリジェントなデータ抽出とエンティティ追跡の実装方法
- 自動回復機能を備えた堅牢なエラー処理の構築方法
- Bright DataのリアルタイムWebデータでエージェントを強化する方法
それでは始めましょう!
ステートレスAI会話の課題
現在のAIエージェントは通常、ステートレスシステムとして動作します。各会話を独立したイベントとして扱うため、履歴コンテキストが欠如し、ユーザーは情報を繰り返し伝える必要があります。その結果、業務効率の低下やユーザーの不満を招きます。さらに、企業は長期データを活用したパーソナライゼーションやサービス改善の機会を逃しています。
データ永続型AIは、すべての対話を構造化されたデータベースに記録することでこの問題を解決します。継続的な記録を保持することで、これらのシステムは過去の文脈を記憶し、特定のエンティティを時間軸で追跡し、過去の対話パターンを活用して一貫性とパーソナライズされたユーザー体験を提供できます。
構築対象:データベース連携型AIエージェントシステム
LangChainとGPT-4を用いてメッセージを処理する、本番環境対応のAIエージェントを構築します。各会話をPostgreSQLに保存し、エンティティとインサイトをリアルタイムで抽出します。セッションを跨いだ完全な会話履歴を保持し、自動再試行システムでエラーを管理します。ログ記録によるモニタリング機能を提供します。
本システムが対応する事項:
- 適切なリレーションシップとインデックスを備えたデータベーススキーマ
- カスタムデータベースツールを備えたLangChainエージェント
- 自動会話永続化とエンティティ抽出
- データ収集のためのバックグラウンド処理パイプライン
- トランザクション管理を伴うエラー処理
- 履歴データを取得するためのクエリインターフェース
- ウェブインテリジェンスのためのBright DataとのRAG統合
前提条件
開発環境のセットアップ:
- Python 3.10 以上。最新の非同期機能と型ヒントに必須
- PostgreSQL 14+またはSQLite 3.35+。データ永続化用データベース
- OpenAI APIキー。GPT-4アクセス用。OpenAI Platformから取得
- LangChain。AIエージェント構築用フレームワーク。ドキュメント参照
- Python仮想環境。依存関係を分離します。
venvドキュメントを参照
環境設定
プロジェクトディレクトリを作成し、依存関係をインストールします:
mkdir database-agent
cd database-agent
python -m venv venv
# macOS/Linux: source venv/bin/activate
# Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
pip install langchain langchain-openai sqlalchemy psycopg2-binary python-dotenv pydanticagent.pyという新しいファイルを作成し、以下のインポートを追加:
import os
import json
import logging
import time
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional
from queue import Queue
from threading import Thread
# SQLAlchemy インポート
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String, Text, DateTime, Float, JSON, ForeignKey, text
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship, Session, declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.pool import QueuePool
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
# LangChain インポート
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain.tools import Tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
# RAG インポート
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
import requests
# 環境設定
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
# ログ設定
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)認証情報を記載した.envファイルを作成:
# データベース設定
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://username:password@localhost:5432/agent_db"
# SQLiteの場合: DATABASE_URL="sqlite:///./agent_data.db"
# APIキー
OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-api-key"
# オプション: Bright Data (ステップ7用)
BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY="your-bright-data-api-key"
# アプリケーション設定
AGENT_MODEL="gpt-4-turbo-preview"
CONNECTION_POOL_SIZE=5
MAX_RETRIES=3必要なもの:
- データベースURL: PostgreSQLまたはSQLiteの接続文字列
- OpenAI APIキー: GPT-4によるエージェント知能化用
- Bright Data APIキー: オプション(ステップ7のリアルタイムWebデータ取得用)
データベース接続型AIエージェントの構築
ステップ1: データベーススキーマの設計
ユーザー、会話、メッセージ、抽出エンティティ用のテーブルを設計します。スキーマは外部キーとリレーションシップを使用してデータ整合性を維持します。
Base = declarative_base()
class User(Base):
"""ユーザープロファイルテーブル - ユーザー情報と設定を保存"""
__tablename__ = 'users'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
user_id = Column(String(255), unique=True, nullable=False, index=True)
name = Column(String(255))
email = Column(String(255))
preferences = Column(JSON, default={})
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
last_active = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow, onupdate=datetime.utcnow)
# リレーションシップ
conversations = relationship("Conversation", back_populates="user", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<User(user_id='{self.user_id}', name='{self.name}')>"
class Conversation(Base):
"""会話セッションテーブル - 個々の会話セッションを追跡します。"""
__tablename__ = 'conversations'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(String(255), unique=True, nullable=False, index=True)
user_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('users.id'), nullable=False)
title = Column(String(500))
summary = Column(Text)
status = Column(String(50), default='active') # active, archived, deleted
meta_data = Column(JSON, default={})
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
updated_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow, onupdate=datetime.utcnow)
# リレーションシップ
user = relationship("User", back_populates="conversations")
messages = relationship("Message", back_populates="conversation", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
entities = relationship("Entity", back_populates="conversation", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Conversation(id='{self.conversation_id}', user='{self.user_id}')>"
class Message(Base):
"""個々のメッセージテーブル - 会話内の各メッセージを格納"""
__tablename__ = 'messages'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('conversations.id'), nullable=False, index=True)
role = Column(String(50), nullable=False) # user, assistant, system
content = Column(Text, nullable=False)
tokens = Column(Integer)
model = Column(String(100))
meta_data = Column(JSON, default={})
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
# Relationships
conversation = relationship("Conversation", back_populates="messages")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Message(role='{self.role}', conversation='{self.conversation_id}')>"
class Entity(Base):
"""会話から抽出された固有表現を格納するテーブル"""
__tablename__ = 'entities'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('conversations.id'), nullable=False, index=True)
entity_type = Column(String(100), nullable=False, index=True) # 人物、組織、場所など
entity_value = Column(String(500), nullable=False)
context = Column(Text)
confidence = Column(Float, default=0.0)
meta_data = Column(JSON, default={})
extracted_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
# リレーションシップ
conversation = relationship("Conversation", back_populates="entities")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Entity(type='{self.entity_type}', value='{self.entity_value}')>"
class AgentLog(Base):
"""エージェント操作ログテーブル - 監視用の操作ログを保存します。"""
__tablename__ = 'agent_logs'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(String(255), index=True)
level = Column(String(50), nullable=False) # INFO, WARNING, ERROR
operation = Column(String(255), nullable=False)
message = Column(Text, nullable=False)
error_details = Column(JSON)
execution_time = Column(Float) # 秒単位
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<AgentLog(level='{self.level}', operation='{self.operation}')>"スキーマは5つのコアテーブルを定義する。Userは柔軟なデータのためのJSON設定付きプロファイルを保存する。Conversationはステータス追跡付きセッションを追跡する。Messageはユーザーとアシスタントのメッセージを区別する役割指標付き個々のやり取りを保持する。Entityは信頼度スコア付き抽出情報を捕捉する。AgentLogは監視のための操作追跡を提供する。外部キーは参照整合性を維持する。頻繁にクエリされるフィールドのインデックスはパフォーマンスを最適化する。cascade="all, delete-orphan"設定は親レコード削除時に関連レコードをクリーンアップする。
ステップ2: データベース接続層の設定
SQLAlchemyでデータベース接続マネージャーを設定します。マネージャーは接続プーリング、ヘルスチェック、信頼性向上のための自動再試行ロジックを処理します。
class DatabaseManager:
"""
データベース接続と操作を管理します。
機能:
- 効率的なリソース使用のための接続プール
- データベース接続性を検証するヘルスチェック
- 自動テーブル作成
"""
def __init__(self, database_url: str, pool_size: int = 5, max_retries: int = 3):
"""
データベースマネージャーを初期化します。
引数:
database_url: データベース接続文字列 (例: 'sqlite:///./agent_data.db')
pool_size: プール内で維持する接続数
max_retries: 失敗した操作に対する最大再試行回数
"""
self.database_url = database_url
self.max_retries = max_retries
# 接続プール機能付きエンジンを作成
self.engine = create_engine(
database_url,
poolclass=QueuePool,
pool_size=pool_size,
max_overflow=10,
pool_pre_ping=True, # 使用前に接続を検証
echo=False # SQLデバッグ時はTrueに設定
)
# セッションファクトリを作成
self.SessionLocal = sessionmaker(
bind=self.engine,
autocommit=False,
autoflush=False
)
logger.info(f"✓ {pool_size}接続プールでデータベースエンジンを作成")
def initialize_database(self):
"""データベース内の全テーブルを作成"""
try:
Base.metadata.create_all(bind=self.engine)
logger.info("✓ データベーステーブル作成成功")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ データベーステーブル作成失敗: {e}")
raise
def get_session(self) -> Session:
"""操作実行用の新規データベースセッションを取得します。"""
return self.SessionLocal()
def health_check(self) -> bool:
"""
データベース接続性を確認します。
戻り値:
bool: データベースが正常な場合True、それ以外の場合False
"""
try:
with self.engine.connect() as conn:
conn.execute(text("SELECT 1"))
logger.info("✓ データベース健全性チェックに合格")
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ データベース健全性チェックに失敗: {e}")
return FalseDatabaseManagerはSQLAlchemyの接続プールを使用して接続を確立します。pool_size=5を設定することで、効率化のため5つの永続接続を維持します。pool_pre_pingオプションは使用前に接続を検証します。これにより古い接続エラーを防ぎます。リトライ機構は指数関数的バックオフで最大3回まで失敗した操作を再試行します。一時的なネットワーク問題を処理します。
ステップ3: LangChainエージェントコアの構築
LangChain を使用して、データベースとやり取りするカスタムツールを備えた AI エージェントを作成します。エージェントは関数呼び出しを使用して情報を保存し、会話履歴を取得します。
class DataPersistentAgent:
"""
データベース永続化機能を備えたAIエージェント。
このエージェントは:
- セッションを跨いだ会話を記憶
- ユーザー情報の保存と取得
- 重要なエンティティの抽出と保存
- 履歴に基づくパーソナライズされた応答を提供
"""
def __init__(
self,
db_manager: DatabaseManager,
model_name: str = "gpt-4-turbo-preview",
temperature: float = 0.7
):
"""
データ永続化エージェントを初期化します。
引数:
db_manager: データベース管理インスタンス
model_name: 使用するLLMモデル (デフォルト: gpt-4-turbo-preview)
temperature: 応答生成時のモデル温度
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.model_name = model_name
# LLMの初期化
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(
model=model_name,
temperature=temperature,
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
)
# エージェント用ツールの作成
self.tools = self._create_agent_tools()
# エージェントプロンプトの作成
self.prompt = self._create_agent_prompt()
# メモリの初期化
self.memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=True
)
# エージェントの作成
self.agent = create_openai_functions_agent(
llm=self.llm,
tools=self.tools,
prompt=self.prompt
)
# エージェント実行器の作成
self.agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=self.agent,
tools=self.tools,
memory=self.memory,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
logger.info(f"✓ データ永続化エージェントを {model_name} で初期化")
def _create_agent_tools(self) -> List[Tool]:
"""データベース操作用のカスタムツールを作成"""
def save_user_info(user_data: str) -> str:
"""ユーザー情報をデータベースに保存します。"""
try:
data = json.loads(user_data)
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=data['user_id']).first()
if not user:
user = User(**data)
session.add(user)
else:
for key, value in data.items():
setattr(user, key, value)
session.commit()
session.close()
return f"✓ ユーザー情報の保存に成功しました"
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"ユーザー情報の保存に失敗しました: {e}")
return f"❌ ユーザー情報の保存エラー: {str(e)}"
def retrieve_user_history(user_id: str) -> str:
"""ユーザーの会話履歴を取得します。"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
return "ユーザーが見つかりません"
conversations = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(user_id=user.id).order_by(Conversation.created_at.desc()).limit(5).all()
history = []
for conv in conversations:
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conv.id).all()
history.append({
'conversation_id': conv.conversation_id,
'created_at': conv.created_at.isoformat(),
'message_count': len(messages),
'summary': conv.summary
})
session.close()
return json.dumps(history, indent=2)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"履歴取得に失敗しました: {e}")
return f"❌ 履歴取得エラー: {str(e)}"
def extract_entities(text: str) -> str:
"""テキストからエンティティを抽出し、データベースに保存する。"""
try:
entities = []
# 簡易キーワード抽出(適切なNER処理に置き換える)
keywords = ['important', 'key', 'critical']
for keyword in keywords:
if keyword in text.lower():
entities.append({
'entity_type': 'keyword',
'entity_value': keyword,
'confidence': 0.8
})
return json.dumps(entities, indent=2)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"エンティティ抽出に失敗しました: {e}")
return f"❌ エンティティ抽出エラー: {str(e)}"
tools = [
Tool(
name="SaveUserInfo",
func=save_user_info,
description="ユーザー情報をデータベースに保存します。入力はユーザー詳細を含むJSON文字列である必要があります。"
),
Tool(
name="RetrieveUserHistory",
func=retrieve_user_history,
description="データベースからユーザーの会話履歴を取得します。入力はuser_idである必要があります。"
),
Tool(
name="ExtractEntities",
func=extract_entities,
description="テキストから重要なエンティティを抽出しデータベースに保存します。入力は解析対象のテキストである必要があります。"
)
]
return tools
def _create_agent_prompt(self) -> ChatPromptTemplate:
"""エージェントプロンプトテンプレートを作成します。"""
system_message = """あなたは会話内容を記憶し学習できるAIアシスタントです。
以下のツールを利用できます:
- SaveUserInfo: 将来の会話のために記憶すべきユーザー情報を保存
- RetrieveUserHistory: ユーザーとの過去の会話を参照
- ExtractEntities: 会話から重要な情報を抽出して保存
これらのツールを活用し、パーソナライズされた文脈に応じた応答を提供してください。応答前には必ずユーザーとの過去の会話履歴を確認してください。
将来の会話のために重要な情報を積極的に保存してください。"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system_message),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad")
])
return prompt
def chat(self, user_id: str, message: str, conversation_id: Optional[str] = None) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
チャットメッセージを処理し、データベースに永続化します。
このメソッドが扱う処理:
1. 会話の作成または取得
2. ユーザーメッセージのデータベースへの保存
3. エージェント応答の生成
4. エージェント応答のデータベースへの保存
5. 監視のための操作のログ記録
引数:
user_id: ユーザーの一意の識別子
message: ユーザーのメッセージテキスト
conversation_id: 既存の会話を引き継ぐためのオプションの会話ID
戻り値:
dict: conversation_id, response, execution_time を含む
"""
start_time = datetime.utcnow()
try:
# 会話の取得または作成
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
if conversation_id:
conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation_id).first()
else:
# 新規会話の作成
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
user = User(user_id=user_id, name=user_id)
session.add(user)
session.commit()
conversation = Conversation(
conversation_id=f"conv_{user_id}_{datetime.utcnow().timestamp()}",
user_id=user.id,
title=message[:100]
)
session.add(conversation)
session.commit()
# ユーザーメッセージを保存
user_message = Message(
conversation_id=conversation.id,
role="user",
content=message,
model=self.model_name
)
session.add(user_message)
session.commit()
# エージェント応答を取得
response = self.agent_executor.invoke({
"input": f"[User ID: {user_id}] {message}"
})
# アシスタントメッセージを保存
assistant_message = Message(
conversation_id=conversation.id,
role="assistant",
content=response['output'],
model=self.model_name
)
session.add(assistant_message)
session.commit()()
# 操作のログ記録
execution_time = (datetime.utcnow() - start_time).total_seconds()
log_entry = AgentLog(
conversation_id=conversation.conversation_id,
level="INFO",
operation="chat",
message="チャット処理成功",
execution_time=execution_time
)
session.add(log_entry)
session.commit()
# セッション終了前に conversation_id を抽出
conversation_id_result = conversation.conversation_id
session.close()
logger.info(f"✓ ユーザー {user_id} のチャット処理を {execution_time:.2f}秒で完了")
return {
'conversation_id': conversation_id_result,
'response': response['output'],
'execution_time': execution_time
}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ チャット処理エラー: {e}")
# エラーをログに記録
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
error_log = AgentLog(
conversation_id=conversation_id or "unknown",
level="ERROR",
operation="chat",
message=str(e),
error_details={'exception_type': type(e).__name__}
)
session.add(error_log)
session.commit()
session.close()
raiseDataPersistentAgentは、LangChainの関数呼び出しエージェントをデータベースツールでラップします。SaveUserInfoツールはUserレコードの作成または更新によりユーザーデータを永続化します。RetrieveHistoryツールは過去の会話をクエリしコンテキストを提供します。システムプロンプトはエージェントに対し、情報の保存と履歴確認を積極的に行うよう指示します。ConversationBufferMemoryはセッション内の短期コンテキストを維持します。データベースストレージはセッションを跨いだ長期的な永続性を提供します。
ステップ3.5: データ収集モジュールの作成
会話からデータを抽出し構造化するツールを構築します。コレクターはLLMを用いて要約を生成し、嗜好を抽出し、エンティティを識別します。
class DataCollector:
"""
エージェント会話からデータを収集・構造化します。
このモジュールは:
- 会話要約を生成
- 会話履歴からユーザー嗜好を抽出
- 固有名詞を識別・保存
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager, llm: ChatOpenAI):
"""
データコレクターを初期化します。
引数:
db_manager: データベース管理インスタンス
llm: テキスト分析用言語モデル
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.llm = llm
logger.info("✓ データコレクター初期化完了")
def extract_conversation_summary(self, conversation_id: str) -> str:
"""
LLMを使用して会話の要約を生成・保存する。
引数:
conversation_id: 要約対象の会話ID
戻り値:
str: 生成された要約テキスト
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation_id).first()
if not conversation:
return "会話が見つかりません"
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation.id).all()
# 会話テキストの構築
conv_text = "n".join([
f"{msg.role}: {msg.content}" for msg in messages
])
# LLMによる要約生成
summary_prompt = f"""以下の会話を2~3文で要約し、主要なトピックと結果を捉えてください:
{conv_text}
要約:"""
summary_response = self.llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=summary_prompt)])
summary = summary_response.content
# 要約で会話更新
conversation.summary = summary
session.commit()
session.close()
logger.info(f"✓ 会話 {conversation_id} の要約を生成しました")
return summary
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"要約生成に失敗しました: {e}")
return ""
def extract_user_preferences(self, user_id: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
会話履歴からユーザー設定を抽出して保存する。
引数:
user_id: 分析対象ユーザーのID
戻り値:
dict: 抽出された設定
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
return {}
# 最近の会話取得
conversations = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(user_id=user.id).order_by(Conversation.created_at.desc()).limit(10).all()
all_messages = []
for conv in conversations:
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conv.id).all()
all_messages.extend([msg.content for msg in messages if msg.role == "user"])
if not all_messages:
return {}
# LLMを用いた嗜好分析
analysis_prompt = f"""ユーザーの以下のメッセージを分析し、嗜好、興味、コミュニケーションスタイルを抽出してください。
メッセージ:
{chr(10).join(all_messages[:20])}
以下の構造を持つJSONオブジェクトを返してください:
{{
"interests": ["interest1", "interest2"],
"communication_style": "description",
"preferred_topics": ["topic1", "topic2"],
"language_preference": "language"
}}"""
response = self.llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=analysis_prompt)])
try:
# レスポンスからJSONを抽出
content = response.content
if '```json' in content:
content = content.split('```json')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
elif '```' in content:
content = content.split('```')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
preferences = json.loads(content)
# ユーザー設定を更新
user.preferences = preferences
session.commit()
logger.info(f"✓ ユーザー {user_id} の設定を抽出しました")
return preferences
except json.JSONDecodeError:
logger.warning("設定のJSONパースに失敗しました")
return {}
finally:
session.close()
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"設定の抽出に失敗しました: {e}")
return {}
def extract_entities_with_llm(self, conversation_id: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
LLMを使用して固有表現を抽出します。
引数:
conversation_id: 分析対象の会話のID
戻り値:
list: 抽出されたエンティティのリスト
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation_id).first()
if not conversation:
return []
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation.id).all()
conv_text = "n".join([msg.content for msg in messages])
# LLMを使用してエンティティを抽出
entity_prompt = f"""以下の会話から固有名詞を抽出してください。特定対象:
- 人物 (PERSON) (PERSON)
- 組織 (ORG)
- 場所 (LOC)
- 日付 (DATE)
- 製品 (PRODUCT)
- 技術 (TECH)
会話:
{conv_text}
以下の形式でエンティティのJSON配列を返す:
[
{{"type": "PERSON", "value": "John Doe", "context": "チームリーダーとして言及"}},
{{"type": "ORG", "value": "Acme Corp", "context": "顧客企業"}}
]"""
response = self.llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=entity_prompt)])
try:
content = response.content
if '```json' in content:
content = content.split('```json')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
elif '```' in content:
content = content.split('```')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
entities_data = json.loads(content)
# エンティティをデータベースに保存
saved_entities = []
for entity_data in entities_data:
entity = Entity(
conversation_id=conversation.id,
entity_type=entity_data['type'],
entity_value=entity_data['value'],
context=entity_data.get('context', ''),
confidence=0.9 # LLM抽出は信頼度が高い
)
session.add(entity)
saved_entities.append(entity_data)
session.commit()
session.close()
logger.info(f"✓ 会話 {conversation_id} から {len(saved_entities)} 個のエンティティを抽出しました")
return saved_entities
except json.JSONDecodeError:
logger.warning("エンティティのJSONパースに失敗しました")
return []
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"エンティティ抽出に失敗: {e}")
return []DataCollectorはLLMを用いて会話を分析します。extract_conversation_summaryメソッドは会話の簡潔な要約を作成します。extract_user_preferencesメソッドはメッセージパターンを分析し、ユーザーの興味やコミュニケーションスタイルを特定します。extract_entities_with_llmメソッドは構造化されたプロンプトを用いて、人物、組織、技術などの固有名詞エンティティを抽出します。抽出された全データは将来参照のためデータベースに保存されます。
ステップ4: スマートデータ処理パイプラインの構築
エージェントをブロックせずにデータ収集を処理するバックグラウンド処理を実装します。このパイプラインはワーカースレッドとキューを使用して要約とエンティティを処理します。
class DataProcessingPipeline:
"""
非同期データ処理パイプライン。
このパイプラインは:
- バックグラウンドで会話を処理
- 要約を生成
- メインフローをブロックせずにエンティティを抽出
- ユーザー設定を定期的に更新
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager, collector: DataCollector, batch_size: int = 10):
"""
処理パイプラインを初期化します。
引数:
db_manager: データベース管理インスタンス
collector: 処理操作用のデータコレクター
batch_size: 各バッチで処理するアイテム数
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.collector = collector
self.batch_size = batch_size
# 処理キュー
self.summary_queue = Queue()
self.entity_queue = Queue()
self.preference_queue = Queue()
# ワーカースレッド
self.workers = []
self.running = False
logger.info("✓ データ処理パイプライン初期化完了")
def start(self):
"""バックグラウンド処理ワーカーを開始"""
self.running = True
# ワーカースレッドの作成
summary_worker = Thread(target=self._process_summaries, daemon=True)
entity_worker = Thread(target=self._process_entities, daemon=True)
preference_worker = Thread(target=self._process_preferences, daemon=True)
summary_worker.start()
entity_worker.start()
preference_worker.start()
self.workers = [summary_worker, entity_worker, preference_worker]
logger.info("✓ 3つのバックグラウンド処理ワーカーを開始しました")
def stop(self):
"""バックグラウンド処理ワーカーを停止します。"""
self.running = False
for worker in self.workers:
worker.join(timeout=5)
logger.info("✓ バックグラウンド処理ワーカーを停止しました")
def queue_conversation_for_processing(self, conversation_id: str, user_id: str):
"""
会話を処理キューに追加します。
引数:
conversation_id: 処理対象の会話ID
user_id: 嗜好抽出対象のユーザーID
"""
self.summary_queue.put(conversation_id)
self.entity_queue.put(conversation_id)
self.preference_queue.put(user_id)
logger.info(f"✓ 処理待ち会話 {conversation_id} をキューに追加")
def _process_summaries(self):
"""会話サマリーの処理を行うワーカー"""
while self.running:
try:
if not self.summary_queue.empty():
conversation_id = self.summary_queue.get()
self.collector.extract_conversation_summary(conversation_id)
self.summary_queue.task_done()
else:
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"要約ワーカーでエラー: {e}")
def _process_entities(self):
"""エンティティ抽出処理ワーカー。"""
while self.running:
try:
if not self.entity_queue.empty():
conversation_id = self.entity_queue.get()
self.collector.extract_entities_with_llm(conversation_id)
self.entity_queue.task_done()
else:
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"エンティティワーカーでエラー: {e}")
def _process_preferences(self):
"""ユーザープリファレンスの処理を行うワーカー。"""
while self.running:
try:
if not self.preference_queue.empty():
user_id = self.preference_queue.get()
self.collector.extract_user_preferences(user_id)
self.preference_queue.task_done()
else:
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"プリファレンスワーカーでエラー: {e}")
def get_queue_status(self) -> Dict[str, int]:
"""
現在のキューサイズを取得します。
戻り値:
dict: 各処理タイプのキューサイズ
"""
return {
'summary_queue': self.summary_queue.qsize(),
'entity_queue': self.entity_queue.qsize(),
'preference_queue': self.preference_queue.qsize()
}ProcessingPipelineはデータ収集とメッセージ処理を分離します。会話が完了すると、すぐに処理されるのではなくキューに追加されます。別々のワーカースレッドがこれらのキューからアイテムを取得し、バックグラウンドで処理します。これにより、データ収集がエージェントの応答を妨げるのを防ぎます。daemon=Trueの設定により、メインプログラム終了時にワーカーが確実に終了します。キュー状態の監視は処理のバックログを追跡するのに役立ちます。
ステップ5: リアルタイム監視とロギングの追加
エージェントのパフォーマンス追跡、エラー検出、レポート生成を行う監視システムを構築します。モニターはログを分析し、運用上の洞察を提供します。
class AgentMonitor:
"""
リアルタイム監視とメトリクス収集。
このモジュールは:
- パフォーマンスメトリクスを追跡
- システムの健全性を監視
- 分析レポートを生成
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager):
"""
エージェントモニターを初期化。
引数:
db_manager: データベースマネージャーインスタンス
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
logger.info("✓ エージェントモニター初期化完了")
def get_performance_metrics(self, hours: int = 24) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
指定期間のパフォーマンスメトリクスを取得。
引数:
hours: 遡る時間数 (時間単位)
戻り値:
dict: 操作回数やエラー率を含むパフォーマンスメトリクス
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
cutoff_time = datetime.utcnow() - timedelta(hours=hours)
# ログのクエリ
logs = session.query(AgentLog).filter(
AgentLog.created_at >= cutoff_time
).all()
# メトリクスを計算
total_operations = len(logs)
error_count = len([log for log in logs if log.level == "ERROR"])
avg_execution_time = sum([log.execution_time or 0 for log in logs]) / max(total_operations, 1)
# 会話数の取得
conversations = session.query(Conversation).filter(
Conversation.created_at >= cutoff_time
).count()
messages = session.query(Message).join(Conversation).filter(
Message.created_at >= cutoff_time
).count()
session.close()
metrics = {
'time_period_hours': hours,
'total_operations': total_operations,
'error_count': error_count,
'error_rate': error_count / max(total_operations, 1),
'avg_execution_time': avg_execution_time,
'conversations_created': conversations,
'messages_processed': messages
}
logger.info(f"✓ 過去 {hours} 時間のパフォーマンスメトリクスを生成しました")
return metrics
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"パフォーマンスメトリクスの取得に失敗しました: {e}")
return {}
def health_check(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
ヘルスチェックを実行します。
戻り値:
dict: データベース接続状態やエラー率を含むヘルスステータス
"""
try:
# データベース接続状態を確認
db_healthy = self.db_manager.health_check()
# 直近のエラー率を確認
metrics = self.get_performance_metrics(hours=1)
recent_errors = metrics.get('error_count', 0)
# 全体的な健全性を判定
is_healthy = db_healthy and recent_errors < 10
health_status = {
'status': 'healthy' if is_healthy else 'degraded',
'database_connected': db_healthy,
'recent_errors': recent_errors,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}
logger.info(f"✓ Health check: {health_status['status']}")
return health_status
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"ヘルスチェック失敗: {e}")
return {
'status': 'unhealthy',
'error': str(e),
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}AgentMonitorはシステム運用状況の可観測性を提供します。AgentLogテーブルをクエリすることで、総操作数、エラー率、平均実行時間などのメトリクスを追跡します。get_metricsメソッドは設定可能な時間枠で統計を算出します。get_error_reportメソッドはデバッグ用の詳細なエラー情報を取得します。この監視により、問題の事前検知が可能になります。高いエラー率はユーザーに影響が出る前に調査をトリガーします。
ステップ6: クエリインターフェースの構築
保存されたデータを取得・分析するクエリ機能を構築します。このインターフェースは、会話の検索、エンティティの追跡、分析生成のためのメソッドを提供します。
class DataQueryInterface:
"""
保存されたエージェントデータをクエリするためのインターフェース。
このモジュールは以下のメソッドを提供します:
- ユーザー分析データのクエリ
- 会話履歴の取得
- 特定情報の検索
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager):
"""
クエリインターフェースを初期化します。
引数:
db_manager: データベースマネージャインスタンス
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
logger.info("✓ クエリインターフェース初期化完了")
def get_user_analytics(self, user_id: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
特定のユーザーの分析データを取得します。
引数:
user_id: 分析対象ユーザーのID
戻り値:
dict: 会話数や嗜好を含むユーザー分析データ
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
return {}
# 会話数取得
conversation_count = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(user_id=user.id).count()
# メッセージ数取得
message_count = session.query(Message).join(Conversation).filter(
Conversation.user_id == user.id
).count()
# エンティティ数を取得
entity_count = session.query(Entity).join(Conversation).filter(
Conversation.user_id == user.id
).count()
# 時間範囲を取得
first_conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(
user_id=user.id
).order_by(Conversation.created_at).first()
last_conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(
user_id=user.id
).order_by(Conversation.created_at.desc()).first()
session.close()
analytics = {
'user_id': user_id,
'name': user.name,
'conversation_count': conversation_count,
'message_count': message_count,
'entity_count': entity_count,
'preferences': user.preferences,
'first_interaction': first_conversation.created_at.isoformat() if first_conversation else None,
'last_interaction': last_conversation.created_at.isoformat() if last_conversation else None,
'avg_messages_per_conversation': message_count / max(conversation_count, 1)
}
logger.info(f"✓ ユーザー {user_id} の分析データを生成しました")
return analytics
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"ユーザー分析データの取得に失敗しました: {e}")
return {}QueryInterfaceは保存データにアクセスするメソッドを提供します。get_user_conversationsメソッドは、オプションでメッセージを含めるフル会話履歴を取得します。search_conversationsメソッドは SQLのILIKE演算子を用いてメッセージ内容全体を全文検索します。get_entity_mentionsメソッドは特定のエンティティが言及された全会話を検索します。get_user_analyticsメソッドはユーザー活動に関する統計を生成します。これらのクエリによりダッシュボード構築、レポート生成、パーソナライズされた体験の創出が可能となります。
ステップ7: Bright DataのリアルタイムWebデータを活用したRAG構築
Bright DataのリアルタイムWebインテリジェンスによるRAG機能で、データベース接続型エージェントを強化します。この統合により、会話履歴と最新のWebデータを組み合わせ、より優れた応答を実現します。
class BrightDataRAGEnhancer:
"""
Bright Dataのウェブインテリジェンスでデータ永続型エージェントを強化します。
このモジュールは:
- Bright Dataからリアルタイムウェブデータを取得
- RAG用にウェブデータをベクターストアに取り込み
- ウェブ拡張知識でエージェントを強化
"""
def __init__(self, api_key: str, db_manager: DatabaseManager):
"""
Bright DataでRAGエンハンサーを初期化します。
引数:
api_key: Bright Data APIキー
db_manager: データベースマネージャーインスタンス
"""
self.api_key = api_key
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.base_url = "https://api.brightdata.com"
# RAG用ベクトルストアを初期化
self.embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
self.vector_store = Chroma(
embedding_function=self.embeddings,
persist_directory="./chroma_db"
)
self.text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=200
)
logger.info("✓ Bright Data RAG エンハンサーの初期化完了")
def fetch_dataset_data(
self,
dataset_id: str,
filters: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
limit: int = 1000
) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Bright Data Dataset Marketplace からデータを取得します。
引数:
dataset_id: 取得するデータセットのID
filters: データのオプションフィルター
limit: 取得するレコードの最大数
戻り値:
list: 取得したデータセットのレコード
"""
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
endpoint = f"{self.base_url}/データセット/v3/snapshot/{データセットID}"
params = {
"format": "json",
"limit": limit
}
if filters:
params["filter"] = json.dumps(filters)
try:
response = requests.get(endpoint, headers=headers, params=params)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
logger.info(f"✓ Bright Data データセット {dataset_id} から {len(data)} 件のレコードを取得しました")
return data
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Bright Dataデータセットの取得に失敗しました: {e}")
return []
def ingest_web_data_to_rag(
self,
dataset_records: List[Dict[str, Any]],
text_fields: List[str],
metadata_fields: Optional[List[str]] = None
) -> int:
"""
ウェブデータをRAGベクトルストアに取り込む。
引数:
dataset_records: Bright Dataからのレコード
text_fields: テキストコンテンツとして使用するフィールド
metadata_fields: メタデータに含めるフィールド
戻り値:
int: インジェストされたドキュメントチャンクの総数
"""
try:
documents = []
for record in dataset_records:
# テキストフィールドを結合
text_content = " ".join([
str(record.get(field, ""))
for field in text_fields
if record.get(field)
])
if not text_content.strip():
continue
# メタデータ構築
metadata = {
"source": "bright_data",
"record_id": record.get("id", "unknown"),
"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}
if metadata_fields:
for field in metadata_fields:
if field in record:
metadata[field] = record[field]
# テキストをチャンクに分割
chunks = self.text_splitter.split_text(text_content)
for chunk in chunks:
documents.append({
"content": chunk,
"metadata": metadata
})
# ベクトルストアに追加
if documents:
texts = [doc["content"] for doc in documents]
metadatas = [doc["metadata"] for doc in documents]
self.vector_store.add_texts(
texts=texts,
metadatas=metadatas
)
logger.info(f"✓ {len(documents)} 個の文書チャンクをRAGに取り込み完了")
return len(documents)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"RAGへのウェブデータ取り込みに失敗しました: {e}")
return 0
def create_rag_enhanced_agent(
self,
base_agent: DataPersistentAgent
) -> DataPersistentAgent:
"""
既存エージェントをRAG機能で強化します。
引数:
base_agent: 強化対象のベースエージェント
戻り値:
DataPersistentAgent: RAGツールを付与した強化エージェント
"""
def rag_search(query: str) -> str:
"""会話履歴とウェブデータの両方を検索します。"""
try:
# 会話履歴から取得
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
messages = session.query(Message).filter(
Message.content.ilike(f'%{query}%')
).order_by(Message.created_at.desc()).limit(5).all()
results = []
for msg in messages:
results.append({
'content': msg.content,
'source': 'conversation_history',
'relevance': 0.8
})
session.close()
# ベクターストア(ウェブデータ)から取得
try:
vector_results = self.vector_store.similarity_search_with_score(query, k=5)
for doc, score in vector_results:
results.append({
'content': doc.page_content,
'source': 'web_data',
'relevance': 1 - score
})
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"ベクターストアからの取得に失敗しました: {e}")
if not results:
return "関連する情報は見つかりませんでした。"
# コンテキストのフォーマット
context_text = "nn".join([
f"[{item['source']}] {item['content'][:200]}..."
for item in results[:5]
])
return f"取得したコンテキスト:n{context_text}"
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"RAG検索失敗: {e}")
return f"検索実行エラー: {str(e)}"
# エージェントにRAGツールを追加
rag_tool = Tool(
name="SearchKnowledgeBase",
func=rag_search,
description="会話履歴とリアルタイムWebデータの両方から関連情報を検索します。 入力は検索クエリである必要があります。"
)
base_agent.tools.append(rag_tool)
# 新しいツールでエージェントを再作成
base_agent.agent = create_openai_functions_agent(
llm=base_agent.llm,
tools=base_agent.tools,
prompt=base_agent.prompt
)
base_agent.agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=base_agent.agent,
tools=base_agent.tools,
memory=base_agent.memory,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
logger.info("✓ RAG機能を備えた強化エージェント")
return base_agentBrightDataEnhancerはリアルタイムWebデータをエージェントに統合します。fetch_datasetメソッドはBright Dataマーケットプレイスから構造化データを取得します。ingest_to_ragメソッドはこのデータを処理・分割し、意味検索用にChromaベクトルデータベースに保存します。retrieve_contextメソッドはハイブリッド検索を実行し、データベース履歴とベクトル類似性検索を組み合わせます。create_rag_toolメソッドはこの機能をLangChainツールとしてパッケージ化し、エージェントが利用できるようにします。enhance_agentメソッドは既存エージェントにこのRAG機能を追加します。これによりエージェントは内部会話履歴と最新の外部データの両方を使用して質問に回答できるようになります。
完全なデータ永続化エージェントシステムの実行
すべてのコンポーネントを統合して機能するシステムを作成します。
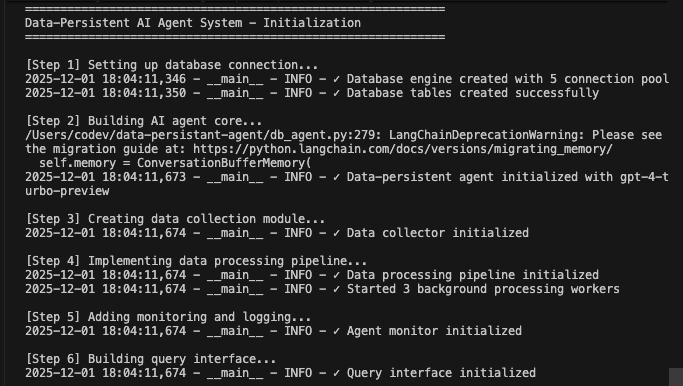
def main():
"""全コンポーネント連携を示すメイン実行フロー"""
print("=" * 60)
print("データ永続化AIエージェントシステム - 初期化")
print("=" * 60)
# ステップ1: データベース初期化
print("n[Step 1] データベース接続設定中...")
db_manager = DatabaseManager(
database_url=os.getenv("DATABASE_URL"),
pool_size=5,
max_retries=3
)
db_manager.initialize_database()
# ステップ2: コアエージェントの初期化
print("n[Step 2] AIエージェントコアの構築中...")
agent = DataPersistentAgent(
db_manager=db_manager,
model_name=os.getenv("AGENT_MODEL", "gpt-4-turbo-preview")
)
# Step 3: データコレクターの初期化
print("n[Step 3] データ収集モジュールの作成中...")
collector = DataCollector(db_manager, agent.llm)
# Step 4: 処理パイプラインの初期化
print("n[Step 4] データ処理パイプラインの実装中...")
pipeline = DataProcessingPipeline(db_manager, collector)
pipeline.start()
# ステップ5: モニタリングの初期化
print("n[Step 5] モニタリングとロギングを追加中...")
monitor = AgentMonitor(db_manager)
# ステップ6: クエリインターフェースの初期化
print("n[Step 6] クエリインターフェースを構築中...")
query_interface = DataQueryInterface(db_manager)
# ステップ7: オプションのBright Data RAG強化
print("n[Step 7] RAG強化 (オプション)...")
bright_data_key = os.getenv("BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY")
if bright_data_key and bright_data_key != "your-bright-data-api-key":
print("Bright DataからリアルタイムWebデータを取得中...")
enhancer = BrightDataRAGEnhancer(bright_data_key, db_manager)
# 例: Webデータの取得と取り込み
web_data = enhancer.fetch_dataset_data(
dataset_id="example_dataset_id",
limit=100
)
if web_data:
enhancer.ingest_web_data_to_rag(
dataset_records=web_data,
text_fields=["title", "content", "description"],
metadata_fields=["url", "published_date"]
)
# RAGでエージェントを強化
agent = enhancer.create_rag_enhanced_agent(agent)
print("✓ Bright Data RAG機能でエージェントを強化")
else:
print("⚠️ Bright Data APIキーが見つかりません - Webデータ統合をスキップ")
print("n" + "=" * 60)
print("デモ会話")
print("=" * 60)
# デモユーザーインタラクション
test_user = "demo_user_001"
# 最初の会話
print("n📝 会話 1:")
response1 = agent.chat(
user_id=test_user,
message="こんにちは! 機械学習について学びたいです。"
)
print(f"エージェント: {response1['response']}n")
# 処理待ちキューへ追加
pipeline.queue_conversation_for_processing(
response1['conversation_id'],
test_user
)
# 2回目の会話
print("📝 会話2:")
response2 = agent.chat(
user_id=test_user,
message="ニューラルネットワークについて教えてくれますか?",
conversation_id=response1['conversation_id']
)
print(f"エージェント: {response2['response']}n")
# バックグラウンド処理を待機
print("⏳ バックグラウンドでデータを処理中...")
time.sleep(5)
print("n" + "=" * 60)
print("分析と監視")
print("=" * 60)
# パフォーマンス指標を取得
metrics = monitor.get_performance_metrics(hours=1)
print(f"n📊 パフォーマンス指標:")
print(f" - 総操作数: {metrics.get('total_operations', 0)}")
print(f" - エラー率: {metrics.get('error_rate', 0):.2%}")
print(f" - 平均実行時間: {metrics.get('avg_execution_time', 0):.2f}秒")
print(f" - 作成された会話: {metrics.get('conversations_created', 0)}件")
print(f" - 処理済みメッセージ数: {metrics.get('messages_processed', 0)}")
# ユーザー分析データを取得
analytics = query_interface.get_user_analytics(test_user)
print(f"n👤 ユーザー分析データ:")
print(f" - 会話数: {analytics.get('conversation_count', 0)}")
print(f" - メッセージ数: {analytics.get('message_count', 0)}")
print(f" - エンティティ数: {analytics.get('entity_count', 0)}")
print(f" - 平均メッセージ数/会話: {analytics.get('avg_messages_per_conversation', 0):.1f}")
# ヘルスチェック
health = monitor.health_check()
print(f"n🏥 システム状態: {health['status']}")
# キュー状態
queue_status = pipeline.get_queue_status()
print(f"n📋 処理キュー:")
print(f" - サマリーキュー: {queue_status['summary_queue']}")
print(f" - エンティティキュー: {queue_status['entity_queue']}")
print(f" - プリファレンスキュー: {queue_status['preference_queue']}")
# パイプラインを停止
pipeline.stop()
print("n" + "=" * 60)
print("データ永続化エージェントシステム - 完了")
print("=" * 60)
print("n✓ 全データがデータベースに永続化されました")
print("✓ バックグラウンド処理が完了しました")
print("✓ システムは本番運用準備完了です")
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("nn⚠️ 正常にシャットダウン中...")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"システムエラー: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()データベース接続エージェントシステムを実行:
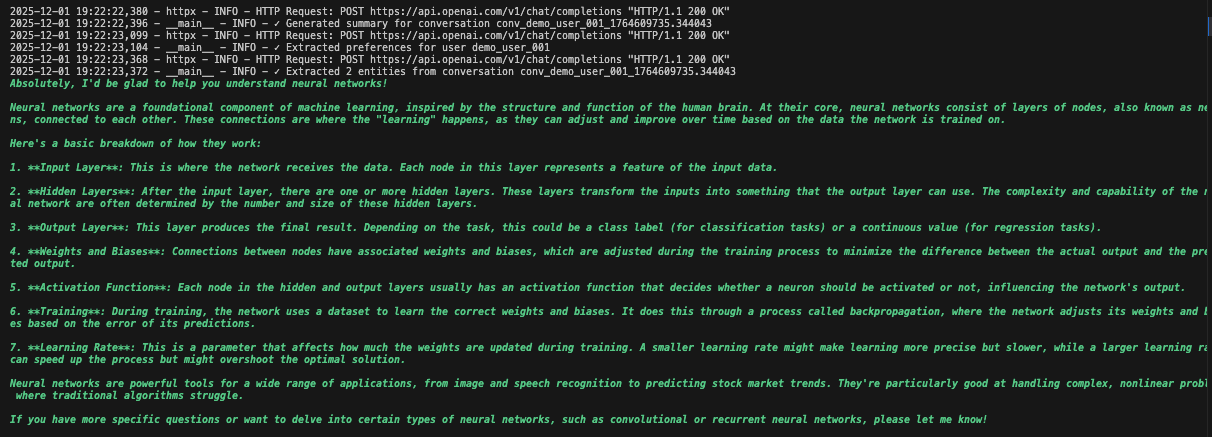
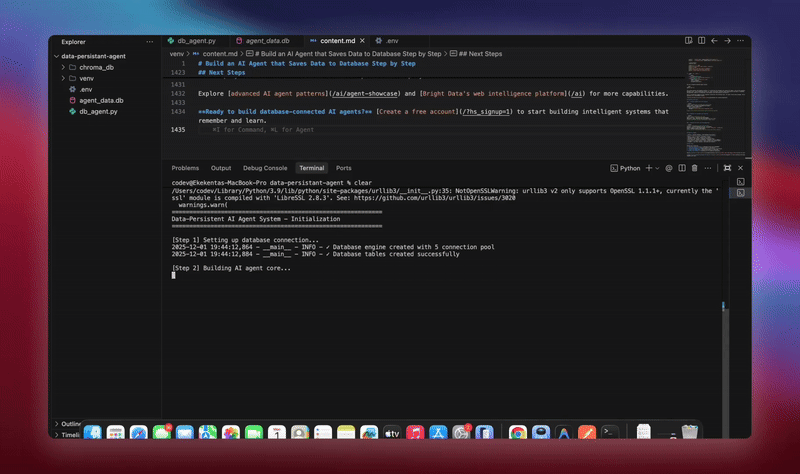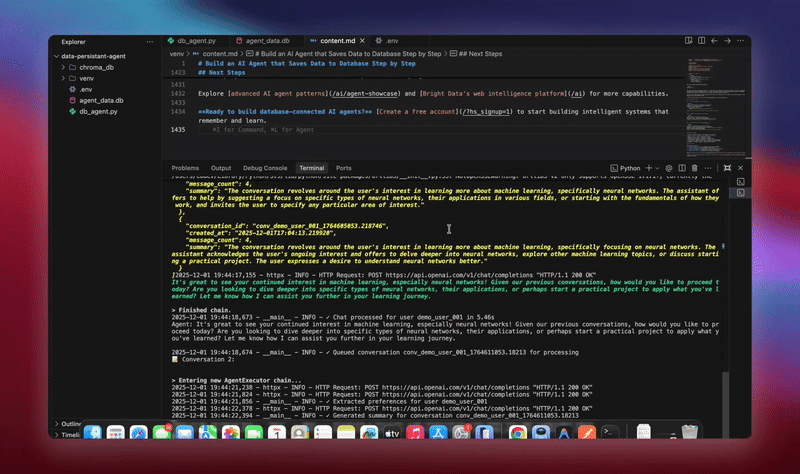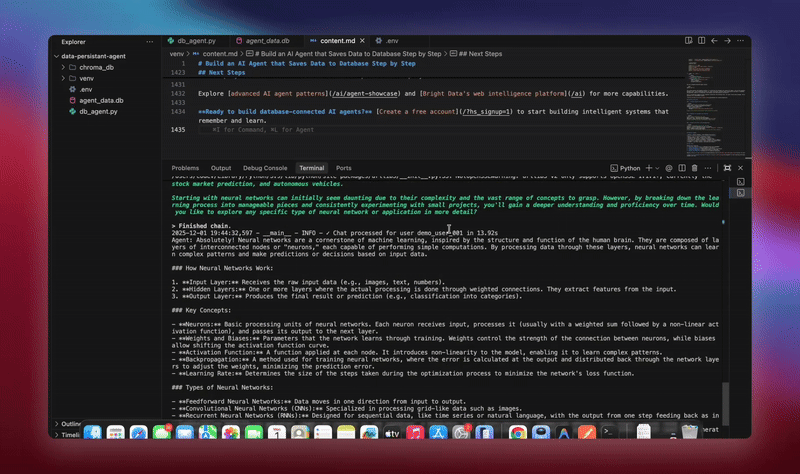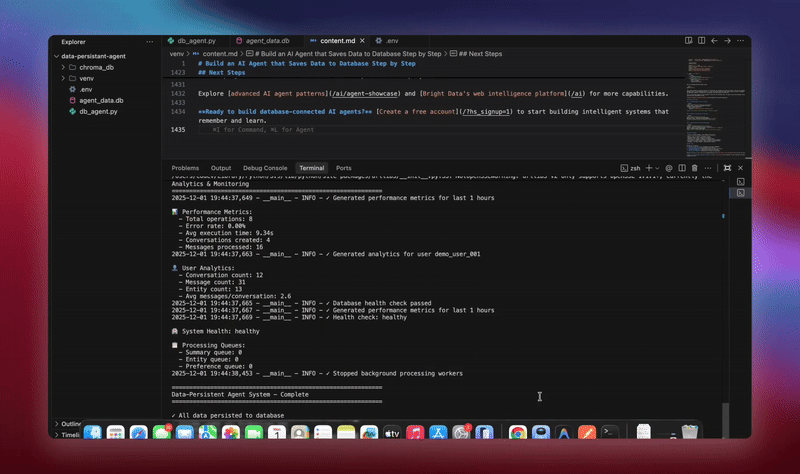
python agent.pyシステムは完全なワークフローを実行します。データベースを初期化し、全てのテーブルを作成します。データベースツールを用いてLangChainエージェントを設定します。処理用のバックグラウンドワーカーを起動します。デモ会話を処理しデータベースに保存します。エンティティを抽出し、バックグラウンドで要約を生成します。リアルタイム分析とメトリクスを表示します。
各コンポーネントが初期化されデータを処理する過程で詳細なログを確認できます。エージェントは全メッセージを保存し、洞察を抽出し、会話の完全な文脈を維持します。
実用的なユースケース
1. 完全履歴付きカスタマーサポート
# エージェントが過去のやり取りを取得
support_agent = DataPersistentAgent(db_manager)
response = support_agent.chat(
user_id="customer_123",
message="接続の問題がまだ発生しています")
# エージェントが過去の接続問題に関する会話を参照2. 学習機能付きパーソナルAIアシスタント
# エージェントが時間の経過とともに好みを学習
query_interface = QueryInterface(db_manager)
analytics = query_interface.get_user_analytics("user_456")
# 対話パターン、好み、共通トピックを表示3. ナレッジベース搭載リサーチアシスタント
# 会話履歴とウェブデータを統合
enhancer = BrightDataEnhancer(api_key, db_manager)
enhancer.ingest_to_rag(research_data, ["title", "abstract", "content"])
agent = enhancer.enhance_agent(agent)
# エージェントは過去の議論と最新研究の両方を参照メリット概要
| 機能 | データベースなし | データベースあり永続性 |
|---|---|---|
| メモリ | 再起動時に消失 | 永続ストレージ |
| パーソナライズ | なし | 完全な履歴に基づく |
| 分析 | 不可 | 完全なインタラクションデータ |
| エラー回復 | 手動介入 | 自動再試行とログ記録 |
| スケーラビリティ | シングルインスタンス | 状態を共有するマルチインスタンス |
| インサイト | セッション終了後に消失 | 抽出および追跡 |
まとめ
データベースへ会話を永続化する本番環境対応のAIエージェントシステムが完成しました。本システムは全インタラクションを保存し、エンティティとインサイトを抽出、完全な会話履歴を維持し、自動エラー回復機能を備えた監視を提供します。
セキュリティ強化のためのユーザー認証追加、分析可視化ダッシュボード構築、意味検索のための埋め込み実装、統合用APIエンドポイント作成、スケーラビリティのためのDockerデプロイなどで機能を拡張できます。モジュール設計により、特定のニーズに合わせたカスタマイズが容易です。
高度なAIエージェントパターンやBright DataのWebインテリジェンスプラットフォームを活用し、さらなる機能を探求してください。
記憶し学習するインテリジェントシステム構築を始めるには、無料アカウントを作成してください。